A drop in income or activity, or a complex personal event, can make it difficult for you, the borrower, to repay your current loans.
In these exceptional circumstances, it is sometimes possible to suspend or defer repayment of the monthly instalments on your loan.
What steps do I need to take?
- Check your loan offer, not all banks allow you to defer part, all or all of your monthly payments. This must be written into your contract.
If this is the case, then we recommend that you check the conditions once or several times a year, age of the loan contract, etc. - Get in touch with your banker to check the terms and conditions and, above all, the costs involved. impact on the total cost of your loan if the repayment period is extended.
What are the possible solutions?
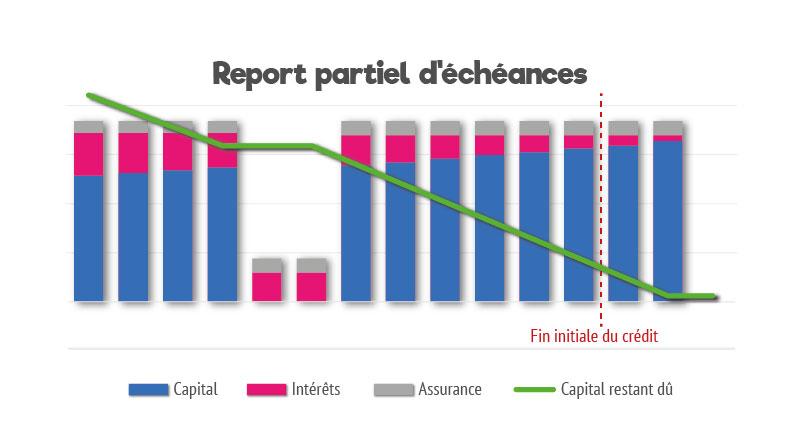
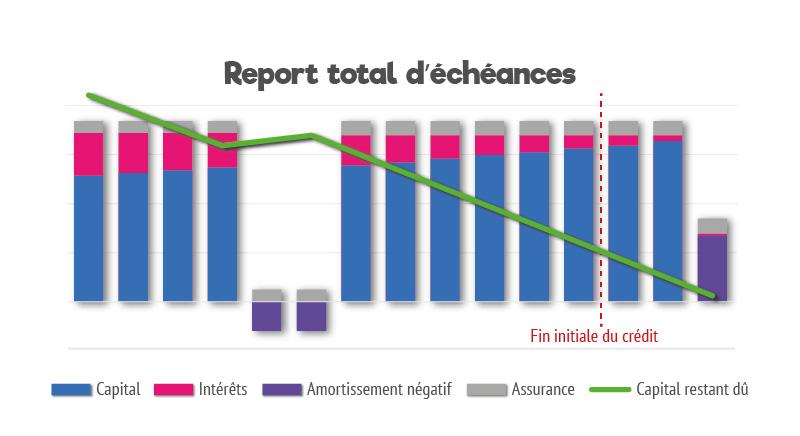
Temporary suspension (or deferment) of your credit
It allows you to suspend payment of your loan instalments for a certain period of time and involves amendment giving you details of the deferment, together with an new depreciation table indicating the adjusted loan amount and term.
Deferment is not possible with all types of loan.
A distinction must be made between :
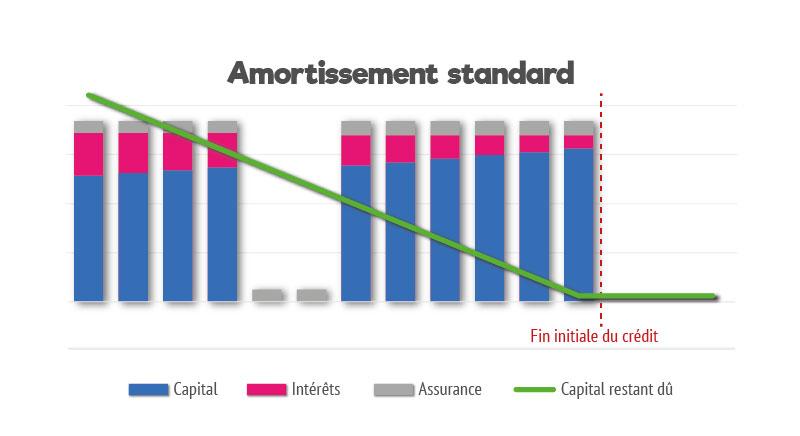
To get a clearer idea of the impact of these two solutions, we invite you to compare them with the standard amortisation of the same mortgage:
In both cases, the deferred monthly instalments are to be paid at the end of the loan, which can extend the initial term of the loan or increase maturities after deferral.
This suspension can range from one to twelve monthsin one or more times.
It can therefore have a high costThis is because the repayment period is extended and therefore generates additional interest.
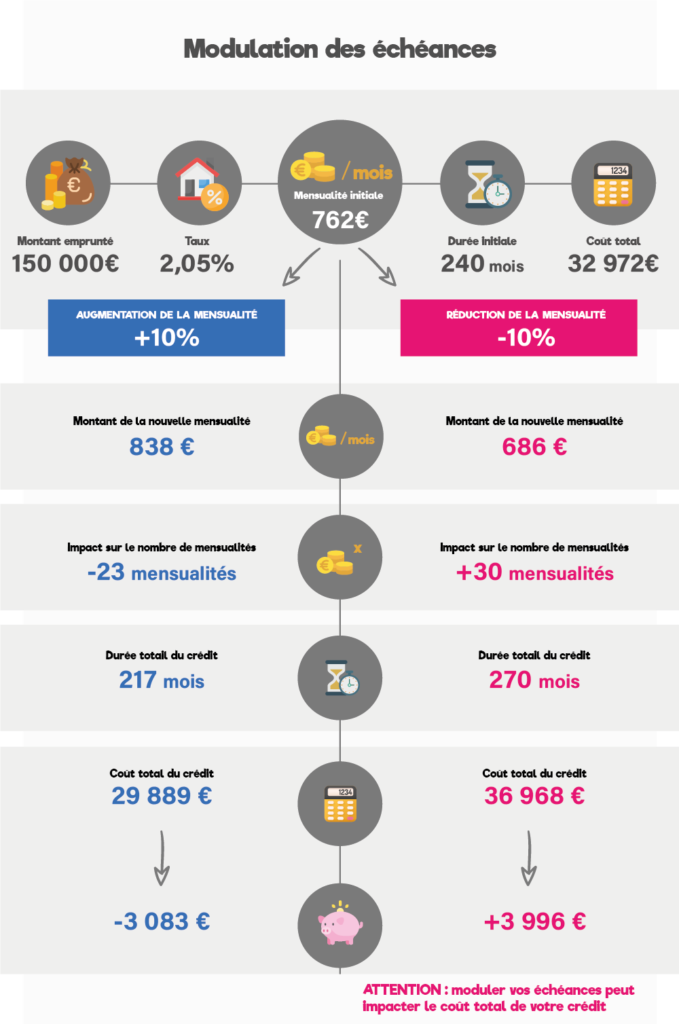
Modulating loan repayments
It allows you to to lower (or increase si vos finances vous le permettent) l’échéance de prêt initialement déterminée.
La modulation n’est possible, à minima qu’après un an d’amortissement.
Les banques donnent la possibilité d’effectuer une seule modulation par an, avec une diminution de mensualité de 10% à 30% (en fonction des banques) et un allongement maximum de prêt de 12 à 24 mois.
Ci-dessous l’exemple d’un couple ayant emprunté 150 000 € sur 20 ans au taux de 2.05 % et voyons l’impact d’une modulation à la hausse ou à la baisse (10 %).
Le coût total du crédit peut également augmenter mais de manière moins significative que lors d’un report d’échéances, dans la mesure où vous continuez de payer une partie des mensualités.
Même si ces aménagements ont un coût, ils restent tout de même des solutions temporaires intéressantes pour faire face à des difficultés financières.
N’hésitez pas à nous solliciter afin que nous puissions étudier ensemble la solution la plus adaptée à votre situation.